Key takeaways
Erectile dysfunction affects about 24% of men in the United States, but it is readily treatable with medication.
Common prescription drugs for ED include the PDE5 inhibitors Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), Stendra (avanafil), and vardenafil.
Some male enhancement supplements and natural remedies may help men with mild ED, but it’s important to first consult a healthcare provider about the pills’ safety and effectiveness.
About 24.2% of men in the United States struggle to maintain or achieve an erection, according to data from the 2021 National Survey of Sexual Wellbeing. The risk of erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, increases with age: More than 50% of men age 75 and older are affected by ED.
Fortunately, ED is readily treatable. Keep reading to find out what prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medicines are available to treat ED and a few natural alternatives for mild ED.
Best erectile dysfunction pills, according to experts
While there’s no single one-size-fits-all pill for erection problems, there is a short list of oral medications that are considered first-line treatments for erectile dysfunction.
The following FDA-approved medications are most commonly prescribed to treat ED:
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Vardenafil (formerly sold as Levitra and Staxyn)
- Avanafil (Stendra)
These FDA-approved ED drugs are classified as phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors or PDE5i). They work by relaxing smooth muscle cells, causing blood vessels to widen and increasing blood flow to the penis so that an erection can be achieved and maintained. It’s important to know that PDE5 inhibitors do not increase sexual desire or trigger sexual arousal. Sexual stimulation is still required—these drugs promote rather than cause erections.
Because they belong to the same drug class, the most common erectile dysfunction medications share very similar side effect profiles. According to StatPearls, the most common adverse effects of PDE5 inhibitors include:
- Mild headache
- Flushing
- Stomach pain
- Altered color vision
- Back pain and body aches
- Dizziness
- Stuffy or runny nose
When a patient asks Bryan Kansas, MD, a board-certified urologist at Urology Austin, which ED medication is the best, he has one answer: “It depends.” The right erectile dysfunction treatment for each person depends on their age, severity of symptoms, concurrent health conditions or health problems, and medical history, he explains.
Sildenafil
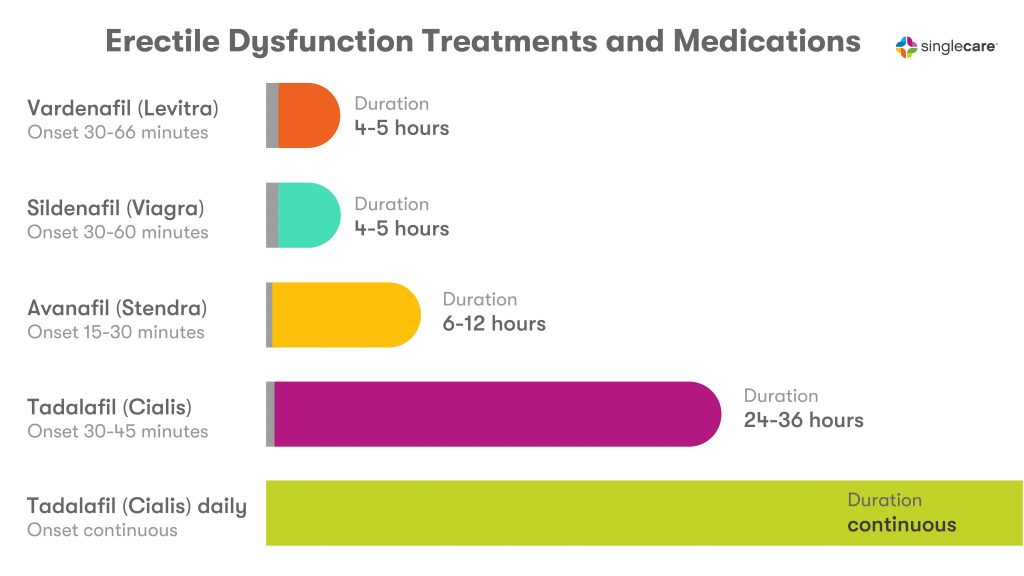
Sildenafil is sold under the brand names Viagra and Revatio, but only generic sildenafil and Viagra are FDA-approved for erectile dysfunction. For ED, an oral sildenafil dose of 25 milligrams (mg) to 100 mg should be taken about 60 minutes before sexual activity. The effects typically last four to five hours.
Compared to the other PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil is associated with a slightly higher risk of flushing and altered color vision, according to StatPearls.
Tadalafil
Tadalafil is a generic drug also sold under the brand names Cialis and Adcirca. Only generic tadalafil and Cialis are approved for the treatment of ED. Adcirca is approved to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (high blood pressure in your lungs). Tadalafil dosage ranges from 10–20 mg taken as needed or 2.5mg to 5 mg taken daily, depending on your prescription. When taken as needed, tadalafil is usually dosed about 1 hour prior to sexual activity. However, the effects can last up to 36 hours.
Vardenafil
Another oral PDE5 inhibitor, vardenafil, is a generic medication. Its brand-name forms, Staxyn and Levitra, have been discontinued. Vardenafil is available in 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg tablets. It should be taken about 60 minutes before sex.
Avanafil
Avanafil is sold under the brand name Stendra. It is the fastest-acting erectile dysfunction pill, reaching maximum concentrations only 30–45 minutes after dosing. It is dosed in 50 mg, 100 mg, or 200 mg tablets that should be taken 30 minutes before sexual activity. Effectiveness typically lasts about 6 hours.
Is Stendra (avanafil) more effective than Viagra?
In a comparison of Stendra versus Viagra, there is not a significant difference in effectiveness, but Stendra has a faster onset of action and shorter duration of action. The main differences are timing and cost.
RELATED: How much does Cialis cost without insurance?
“With the new faster-onset drug Stendra, the patients have more spontaneity, which is a very attractive marketing point,” says Inna Melamed, Pharm.D., a functional medicine practitioner and author of Digestive Reset.
There are a few things to keep in mind when comparing Stendra to Viagra:
- Timing: Stendra can be taken just 15-30 minutes before sexual activity, while Viagra should be taken about an hour before sexual activity.
- Effectiveness: The two drugs are generally considered equally effective, but a small 2022 study found Stendra to be more effective than Viagra after 12 weeks of treatment.
- Cost: Because there is no available generic version of Stendra, Viagra tends to be the more affordable of these two ED drugs.
Which is better: Viagra, Cialis, or Levitra?
It depends. The key differences between all PDE5 inhibitors are the timing of the drugs and how frequently they can be taken. For example:
- Timing: Vardenafil (formerly sold as Levitra), Viagra, and Cialis should be taken one hour before sexual activity, but they can be taken as little as 30 minutes before sexual activity for some patients. The time it takes to work varies by individual.
- Duration: Cialis lasts much longer than Viagra or vardenafil—up to 36 hours compared to 4 to 12 hours.
- Frequency: Cialis can be taken either as needed or daily. Viagra and vardenafil are taken only as necessary and no more than once a day.
RELATED: Cialis vs. Viagra │ Levitra vs. Cialis
How long do ED pills last? A PDE5i Comparison
Other treatments for ED
Your healthcare provider may also recommend one of the following erectile dysfunction treatments.
Alprostadil (Caverject and MUSE)
Alprostadil is a second-line therapy for erectile dysfunction. It is a vasodilator that works by dilating blood vessels to increase blood flow to the penis and allow an erection. This drug is available as a penile injection (Caverject) or a urethral suppository (MUSE).
Testosterone replacement
Erectile dysfunction isn’t always an issue of poor circulation. Low levels of the male sex hormone testosterone can also cause ED. In those cases, testosterone replacement has been shown to improve sexual performance in 61% of patients with underactive gonadal function and erectile function in 36% of these patients, according to a research review published in Androgens: Clinical Research and Therapeutics.
Testosterone replacement combined with other medications and therapies could be even more effective.
Men with low testosterone, or low T, tend to have other symptoms too. Signs of low T include:
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Low libido (decreased sexual desire)
- Delayed ejaculation
- Loss of body hair
- Reduced muscle mass
Anyone who suspects low T should ask their healthcare provider for a blood test. If the hormone level is too low, testosterone therapy may include injections, oral medications, or topical treatments such as gels or creams. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional about the risks versus benefits, as hormone therapy can cause physical side effects, such as enlarged breast tissue or prostate, and mental health side effects like mood swings.
RELATED: The ultimate guide to erectile dysfunction
Nonprescription ED treatment options
There are ways to treat ED without prescription pills, especially if symptoms are mild.
Erectile dysfunction self-care
Some lifestyle changes could help minimize ED symptoms, especially for those with mild ED or who only experience erection difficulties from time to time.
In general, these lifestyle changes support good circulation and overall health, which could help treat or prevent ED:
- Quitting smoking
- Avoiding alcohol
- Exercising more
- Prioritizing good sleep habits
- Practicing stress management strategies such as meditation or breathing exercises
Dr. Melamed also suggests eating more beets, which are rich in nitric oxide—a key chemical mediator in the development of an erection.
ED supplements
Vitamins and supplements have been used as natural remedies to combat erectile dysfunction for many years. But that doesn’t mean their benefits are always well-studied—or even safe.
“Patients should proceed with caution and ideally consult a doctor first,” Dr. Kansas says. “These products can sometimes be helpful for men with very mild ED, but their effectiveness is typically limited compared to prescription options.”
Common herbs and supplements marketed as ED treatment include L-arginine, ginseng, and Yohimbe.
L-arginine
L-arginine is a naturally present amino acid that helps increase the body’s nitric oxide production. This nitric oxide helps blood vessels dilate, which in turn increases blood flow to the penis, thereby facilitating erections.
A 2019 meta-analysis found that study participants who took 1,500–5,000 mg arginine supplements reported significantly improved ED compared with participants who received a placebo or no treatment.
Nitric oxide
“In the naturopathic and integrative world, L-arginine and nitric oxide are often used as first recommended supplements,” Dr. Melamed says. In the body, nitric oxide helps increase blood flow and support healthy erections. However, when it comes to supplementation, it’s important to check brand quality and dosage with a healthcare professional.
Ginseng
Touted as “herbal Viagra,” ginseng has been used for centuries as a remedy for impotence and male sexual function. However, current research suggests that ginseng has “a trivial” effect on ED.
Yohimbe
A 2021 meta-analysis suggested that Yohimbe, which is extracted from the bark of the African Yohimbe tree, has had positive effects on erection issues. However, of the eight studies analyzed, only five used Yohimbe as a monotherapy (the others studied a supplement that included L-arginine or added the antidepressant trazodone). The studies also used a wide range of doses: 5 mg to 100 mg. In other words, further research is needed.
A word of warning: The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) warns that many supplements marketed for sexual enhancement contain high doses of ingredients or even ingredients that are not listed on the product label. If you decide to try an OTC supplement for ED, it’s a good idea to run it past a healthcare professional first.
Over-the-counter ED pills
Discussing erection difficulties with a healthcare provider can be intimidating, so some men seek OTC sexual enhancement pills or male enhancement pills instead of natural supplements or FDA-approved medications. While it might be tempting to pick up pills you can get without a prescription, clinicians and the NCCIH warn against it.
“Many over-the-counter pills lack rigorous testing, so their safety and efficacy may vary widely,” Dr. Kansas says. “Prescription medications, on the other hand, are FDA approved and backed by clinical research. Ultimately, determining the safest and most effective treatment starts with a proper medical evaluation.” It’s helpful to remember that it’s very common for healthcare providers to discuss ED with their male patients. It might be an individual patient’s first time discussing ED, but these are everyday conversations for the prescriber.
As there is a risk that these remedies may interact with other drugs, you should always seek medical advice from your healthcare provider before starting any OTC or natural treatments.
How to choose the right ED pill for you
Erectile dysfunction is treatable. It can also serve as a warning sign of underlying conditions such as cardiovascular disease (heart disease), high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or obesity, according to the Urology Care Foundation. Hence, those who get an early diagnosis can improve their sex life and overall health.
It’s best to speak openly to your healthcare provider or urology specialist to figure out which treatment options will work best based on your symptoms, lifestyle, and the underlying cause.
- Erectile dysfunction prevalence in the United States: Report from the 2021 National Survey of Sexual Wellbeing, The Journal of Sexual Medicine (2024)
- PDE5 Inhibitors, StatPearls (2023)
- Avanafil for erectile dysfunction in elderly and younger adults: differential pharmacology and clinical utility, Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management (2014)
- Efficacy and safety of avanafil as compared with sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A randomized, double blind, multicenter clinical trial, International Journal of Urology (2022)
- The impact of testosterone on erectile dysfunction, Androgens: Clinical Research and Therapeutics (2022)
- Delayed ejaculation, UCLA Health (2025)
- The role of nitric oxide in erectile dysfunction: Implications for medical therapy, The Journal of Clinical Hypertension (2007)
- The potential role of arginine supplements on erectile dysfunction: A systemic review and meta-analysis, The Journal of Sexual Medicine (2019)
- Ginseng for erectile dysfunction, Cochrane Library (2021)
- Yohimbine as a treatment for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Turkish Journal of Urology (2021)
- 4 things to know about dietary supplements marketed for sexual enhancement, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (2025)
- Erectile dysfunction, Urology Care Foundation (2018)